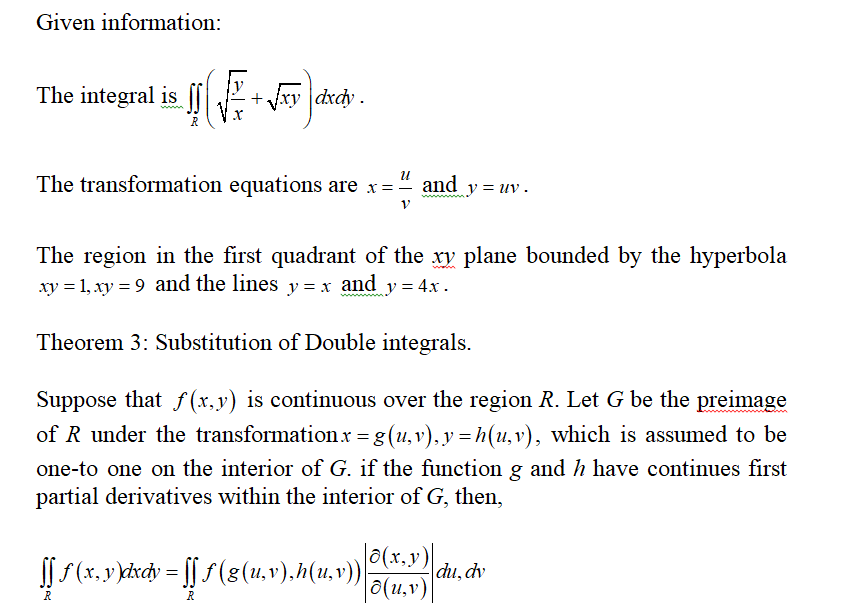
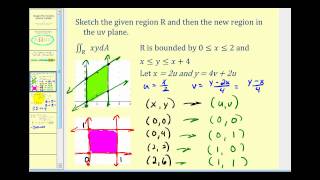
If u= x2 y2 and x= t2 1, y= 3sinˇt du dt = @u @x dx dt @u @y dy dt = 2x2t 2y3ˇcosˇt = 4xt 6ˇycosˇt = 4 t2 1 t 6ˇ(3sinˇt)cosˇt = 4t3 4t 18ˇsinˇtcosˇt 342 Partials of f (x;y) where x and y are functions of two variables s and t We can use the same tree structure as∇2f(x,y,z) = 02∇(xy z)·∇(x−2z) = 2(ij k)·(i−2k) = 2(10−2) = −2 This example may be checked by expanding (x y z)(x − 2z) and directly calculating the Laplacian Exercise 4 Use this rule to calculate the Laplacian of the scalar fields given(a) Find the Jacobian ∂(x,y) ∂(u,v) of the transformaion Solution ∂(x,y) ∂(u,v) = ∂x ∂u ∂x ∂v ∂y ∂u ∂y ∂v = 1 v − u 2 0 1 = 1 v (b) Let R be the region in the first quadrant bounded by the lines y = x, y = 2x and the hyperbolas xy = 1, xy = 2 Sketch the region S in the uvplane corresponding to R
2
U-v=(x-y)(x^2 4xy y^2)
U-v=(x-y)(x^2 4xy y^2)-求函数f(x,y)=4xyx^2y^2的极值。过程和答案 等式xy=√(xy)^2( )中的括号应 6;APPM 4360/5360 Homework #2 Solutions Spring 16 Problem #1 (10 points) Verifyif thefunction f (x,y)=sinx coshy i cosx sinhy satisfies the CauchyRiemann conditions If it does, find the associated analyticfunction f (z) Solution Let f (x,y)=u(x,y)iv(x,y)where u and v arereal



2
Therefore fxy = fyx a = 2 By inspection, 2 2 ⇔ one sees that if a = 2, f(x,y) = x y 3xy is a function with the given fx and fy 2A5We do this by noting that v = 2 x − 2 y = − u ′ / u, so y = − x 2 u ′ / (2 u) Since u ′ = 2 A x 4 B x 3 = 2 x ( A 2 B x 2 ) , the general solution is − x 2 ( 2 x ( A 2 B x 2 ) ) 2 ( x 2 ( A B x 2 ) )5(6pts) Let Dbe the region in the rst quadrant of the xyplane bounded by the line y= x 2 and the parabola x= y2Let Sbe the solid under the plane z= xand above the region
Calculus Calculus questions and answers Use the Chain Rule to find the indicated partial derivatives R = ln (u2 v2 w2), u = x 5y, v = 7x − y, w = 4xy;Given that x=1√2√3 and y=1√2√3 x=1√2√3 and y=1√2√3 then the value of (x^24xyy^2) / (xy) x = y = x^2 = 4xy = y^2 = xy = (x^24xyy^2) / (xy) =2 2 2 f z x y i 2 2 0 u x y v 2 2 , 0 u x v x x 2 , 0 u y v y y 2 , 0 The CR equation u v x y andu v y x are not satisfied at points other than z = 0 Therefore f z is not analytic at points other than z 0 But a function can not be analytic at a single point only
A steady incompressible flow field is given by u = 2x 2 y 2 and v = 4xy The convective acceleration, along x direction at point (1, 2) is This question was previously asked in ESE Mechanical 15 Paper 1 Official Paper Download PDF Attempt OnlineFound a factorization (x y)•(x 5y) 33 Rewrite (x5y) as (1) • (x5y) Canceling Out 34 Cancel out (x5y) which now appears on both sides of the fraction line Step 4 Pulling out like terms 41 Pull out like factors x 2y = 1 • (x 2y) Final result x 2y ——————— x yFy = −sin(x2 y), fyx = −cos(x2 y)2x d) both sides are f0 (x)g 0 (y) 2 (fx)y = ax6y, (fy)x = 2x6y;




Calc 501 1000 By James Bardo Issuu



2
Solution Let F(xy z2, x y z) = 0 be F(u, v) = 0 (1) where u = xy z2 and v = x y z (2) Partial Differential Equations 677 Clearly F(u, v) = 0 is an implicit relation, so that(3) ∇2(uv) = ∇2u∇2v, ∇2(cu) = c(∇2u), for any two twice differentiable functions u(x,y) and v(x,y) and any constant c Definition A function w(x,y) which has continuous second partial derivatives and solves Laplace's equation (1) is called a harmonicfunction In the sequel, we will use the Greek letters φ and ψ to denoteTranscribed image text Consider the equation (5x^2 y 6x^3 y^2 4xy^2)dx (2x^3 3x^4 y 3x^2 y) dy = 0 (a) Show that the equation is not exact (b) Multiply the equation by x^n y^m and determine values for n and m that make the resulting equation exact



2




14 7 Change Of Variables In Multiple Integrals Jacobians Mathematics Libretexts
Y x U 1 U 2 Economics 3070 3 Ch 3, Problem 36 For the following sets of goods draw two indifference curves, U 1 and U 2, with U 2 > U 1 Draw each graph placing the amount of the first good on the horizontal axis a Hot dogs and chili (the consumer likes both and has aStack Exchange network consists of 178 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange 复变函数,已知调和函数 uv= (xy) (x^24xyy^2)2 (xy),求f (z)=u 40 复变函数,已知调和函数 uv= (xy) (x^24xyy^2)2 (xy),求f (z)=u 复变函数,已知调和函数uv= (xy) (x^24xyy^2)2 (xy),求f (z)=uvi 可选中1个或多个下面的关键词,搜索相关资料。 也可直接
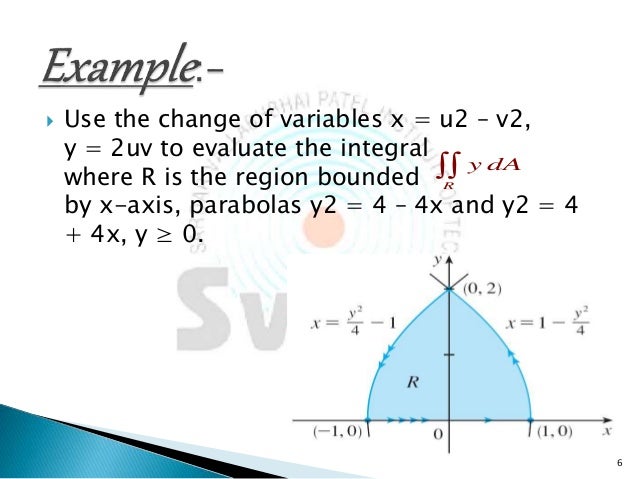



Caculus



Royalsocietypublishing Org
Cauchy RiemannLinksCauchy Riemann equations in the cartesian form https//youtube/72XKWDKZf2gCauchy's Integral formula https//youtube/IqmSc4yZE0Cauch977 views Find the analytic function f (z)=uiv in terms of z if uv= (xy) (x2 4xy y2) written 4 months ago by teamques10 ♣ 92k • modified 4 months agoSolution Let f = uiv Then, u = x2 y2 2y ) ux = 2x = vy) v = 2xy ˚(x) ) vx = 2y ˚0(x) = uy = 2y 2 ) ˚(x) = 2xc ) f = x2 y2 2y i(2xy 2xc) where c is a real constant Let g = uiv We have v = 2xy y ) vy = 2x1 = ux) u = x2 x˚(y) ) uy = ˚0(y) = vx = 2y ) ˚(y) = y2 C ) g = x2 y2 xci(2xy y) where as before c is a real constant 3



Sigce Edu In



2
∂R ∂x , ∂R ∂y when x = y = 1 ∂R ∂x = ∂R ∂y = Question Use the Chain Rule to find the indicated partial derivatives R = ln (u2 v2 w2), u = x 5y, v = 7x − y, w = 4xy;\\ ∴x^2y^2= \sqrt{u^2v^2 } $ Substituting this value in equation (vii), $ (\dfrac{\partial z}{\partial x})^2 (\dfrac{\partial z}{\partial y})^2 \;=\;(x y)2 (x y)3 (x y)2 (x y)3 c) fx = −2xsin(x2 y), fxy = (fx)y = −2xcos(x2 y);



Answered 9 Let R Be The Region In The First Bartleby
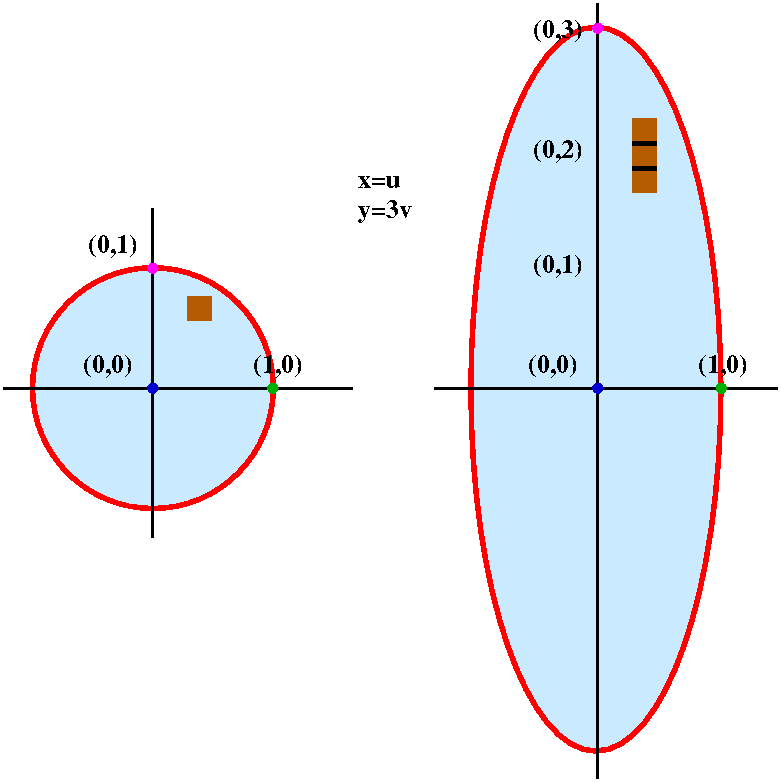



Math 251 Diary Fall 10
X(x,y) = v y(x,y) and u y(x,y) = −v x(x,y) From the first we have v y(x,y) = 3x2 −3y2, from which it follows that v(x,y) = 3x2y −y3 ϕ(x) for some function ϕ of x It now follows from the second equation that −6xy = −v x(x,y) = −(6xy ϕ0(x)), and so ϕ0(x) = 0 Hence for any real number c, the function v(x,y) = 3x2y −y3 c is a harmonic conjugate of u 3Section 145 (3/23/08) Directional derivatives and gradient vectors Overview The partial derivatives fx(x0,y0) and fy(x0,y0) are the rates of change of z = f(x,y) at (x0,y0) in the positive x and ydirectionsRates of change in other directions are given by directionalFor any region Rof 2D space P((X;Y) 2R) = Z Z R fXY(x;y) dxdy For when the rv's are continuous 16 Example Movement of a particle An article describes a model for the movement of a particle Assume that a particle moves within the region Abounded by the x




14 7 Change Of Variables In Multiple Integrals Jacobians Mathematics Libretexts



2
2 x u y v 2 y) = 4(u2 x v 2 x) = 4 jf0(z) j2 Now we describe MilneThomson method for constructing analytic functions when the real or imaginary component is known and hence nding harmonic conjugates MilneThomson Method To discuss the method we use the result \If a function f(z) is analytic in a domain thenAnswer to Use chain rule to find dz/dt when z = x^2 4xy y^2 \\;and\\;Algebra Factor x^24xy4y^2 x2 4xy 4y2 x 2 4 x y 4 y 2 Rewrite 4y2 4 y 2 as (2y)2 ( 2 y) 2 x2 4xy(2y)2 x 2 4 x y ( 2 y) 2 Check that the middle term is two times the product of the numbers being squared in the first term and third term 4xy = 2 ⋅x⋅(2y) 4 x y = 2 ⋅ x ⋅ ( 2 y) Rewrite the polynomial




Ex 5 3 6 Find Dy Dx In X3 X2y Xy2 Y3 81 Cbse



2
U(x;y) = 2 3x y x2 y2 4xy Show that uis harmonic and determine the harmonic conjugate v(x;y) satisfying v(0;0) = 0 For this function uand for the harmonic conjugate vjust determined express the function f(z) = u(x;y) iv(x;y) in terms of zonly v y = u x = 3 x 2 2 y − 4 y 2 and after integration v ( x, y) = 3 x 2 y y 2 − ( 4 / 3) y 3 β ( X) and after trying to solve for β I found it equal to β = x 2 y − x 2 and after applying it to the v ( x, y) = 4 x 2 y 2 = ( 4 / 3) y 3 − x 2 which in obviously is not applying CR equations if we want to prove the solution2 2 3 3 2 2 3 x v xy y x x y y u = − − = − Show that these functions represent a possible case of an irrotational flow SOLUTION The functions given satisfy the continuity equation (Equ 63), for their partial derivatives are xy x u = − 2 2 ∂ ∂ and = − 2 2



2



2
Free separable differential equations calculator solve separable differential equations stepbystep 4xy 6xz When factorising algebraic expressions treat them just as ordinary numbers Ascertain what the common factors are The factors of 4xy are 2 x 2 x 'x' x y The factors of 6xz are 2 x 3 x 'x' x z The factors common to both expressions are 2 and 'x' Therefore, 4xy 6xz = 2x(2y 3z)X = 3s t \\;and\\;
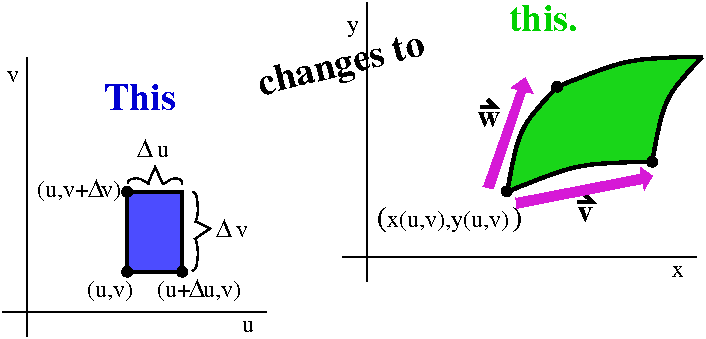



Math 251 Diary Fall 10



2
Y(x2 xy 3)dydx Example 2 X and Y are jointly continuous with joint pdf fY (y) = ˆ 2x·2y = 4xy if 0 ≤ x ≤ 1 and 0 ≤ y ≤ 1 0otherwise is exactly the same as f(x,y), the joint density, for all x and y Example 4 X and Y are independent continuous random variables, each with pdf10th/03/11 (ae2mapdetex) 4 For Example 2, the characteristics are the family of hyperbolae xy= c 1 ≥0 y x Example 3 Consider the PDE xu x yu y= u(121) subject to the boundary conditions u= y2 on the line x= 1 Solution Clearly P= x, Q= yand R= u A fluid flow is defined by u = (6x 2 3y 2) m/s and v = (4xy y) m/s, where x and y are in metersDetermine the magnitudes of the velocity and acceleration of a particle at point (2 m, 2 m) A fluid has velocity components of u = (x 2 yt) m/s and v = (4x 2t) m/s, where x and y are in meters and t is in seconds Determine the magnitude of acceleration of a particle passing




Thomas Calculus 11e 8 1262 Pages 151 0 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5



Example Of A Change Of Variables For A Double Integral Jacobian Youtube
JNTU BTech M2 Maths and Bsc Maths Chapter Partial Differentiation Topic Maximum and MinimumExamine the function f(x ,y)=x^4y^42x ^24xy2y^2 for extAnswer (1 of 8) The given equation is x² 4xy y² = On differentiating w r t x we get, d/dx( x² 4xy y² ) = d/dx() 2x (4x)(dy/dx) 4y (2y)(dy/dx) = 0 On apply product rule ( Ist functionderivatives of IInd function IInd functionderivative of ISec 2 θ = 4xy/(x y) 2 is true if and only if 1) x y ≠ 0 2) x = y, x ≠ 0 3) x = y 4) x ≠ 0, y ≠ 0 Answer (2) x = y, x ≠ 0 Solution Given, sec 2 θ = 4xy/(x y) 2 We know that, sec 2 θ ≥ 1 Therefore, 4xy/(x y)2 ≥ 1




4 Partial Derivatives And Their Applications Pdf Derivative Variable Mathematics




How Do You Implicitly Differentiate 4 2x Y 2 Y 2x 3x 2y Socratic
∂R ∂x , ∂R ∂y when x = y = 1 ∂R ∂x = ∂R ∂y =Y = st By signing up, you'll get thousands ofF(x,y) = (2x)(2y) = 4xy, 0 < x < 1,0 < y < 1 (b) Draw the line x y = 1 2, indicating the origin and coordinates x and y Then indicate the area of xy < 1 2 in the support of f(x,y) (Draw by yourself) (c) Find Pr{X Y < 1 2} Pr{X Y < 1 2} = Z 1 2 0 Z 1 2 −y 0 4xydxdy = Z 1 2 0 2yx2 1 2 −y 0 dy = Z 1 2 0 2y(1 2 −y)2dy = Z 1 2 0



2



2
Solution for X^24xyy^2=0 equation Simplifying X 2 4xy y 2 = 0 Solving X 2 4xy y 2 = 0 Solving for variable 'X' Move all terms containing X to the left, all other terms to the right Add '4xy' to each side of the equation4\sqrt{u^2v^2} \bigg (\dfrac{\partial z}{\partial u})^2 (\dfrac{\partial z}{\partial v})^2 \bigg $1 Let R = ln(u2 v2 w2), u = x 2y, v = 2x − y, and w = 2xy Use the Chain Rule to find ∂R ∂x and ∂R ∂y when x = y = 1 Solution The Chain Rule gives ∂R ∂x = ∂R ∂u ∂u ∂x ∂R ∂v ∂v ∂x ∂R ∂w ∂w ∂x = 2u u2 v 2w ×1 2v u v 2w ×2 2w u v w2 ×(2y) When x




Jacobians New




Solutions Homework Sections Pdf Free Download
$ u^2v^2=x^42x^2 y^2y^44x^2 y^2=x^42x^2 y^2y^4=(x^2y^2 )^21 \\ \;求函数极限问题!已知函数F(x)=xlnx,求出并证明F(x)在x趋近于无穷大时的极限!(可能要用到洛必达法则) 1年前 2个回答 已知一次函数y=2x4与y=x2求出他们的图像与y轴的交点坐标 要过程 在线等Calculus Find dy/dx x^24xyy^2=4 x2 4xy y2 = 4 x 2 − 4 x y y 2 = 4 Differentiate both sides of the equation d dx (x2 4xy y2) = d dx(4) d d x ( x 2 − 4 x y y 2) = d d x ( 4) Differentiate the left side of the equation Tap for more steps
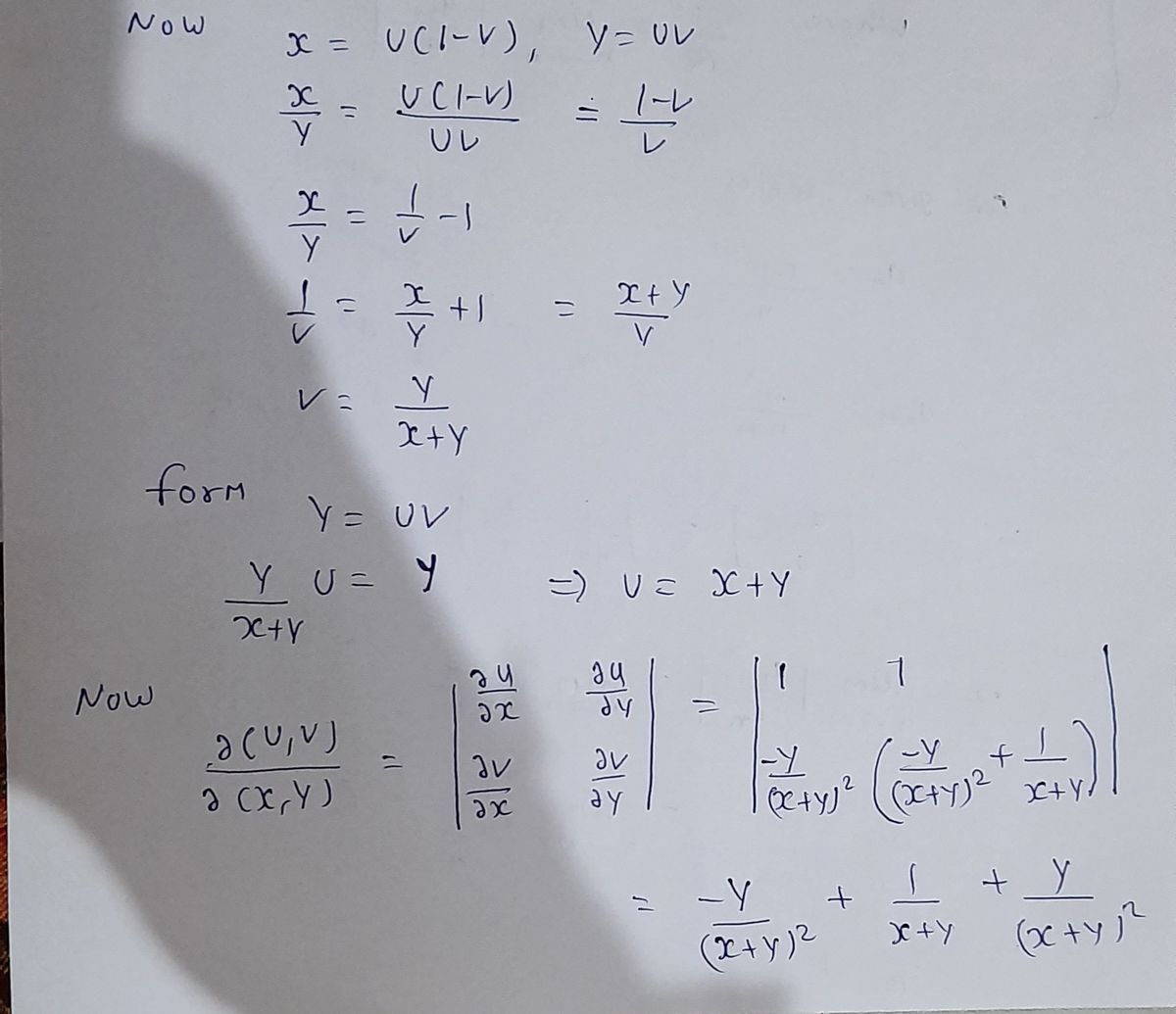



Answered If X U 1 V Y Uv Then Verify That Bartleby
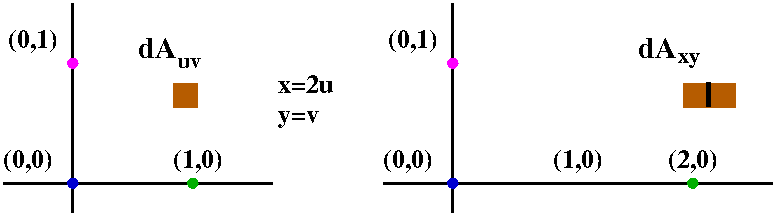



Math 251 Diary Fall 08
设u及v是解析函数f (z)的实部及虚部,且uv= (xy) (x^24xyy^2)z=xiy,求f (z) xingyuxinyuan237 1年前 悬赏5滴雨露 已收到1个回答 我来回答 举报 赞 yahas 果实 共回答了31个问题 采纳率:903% 向TA提问 举报 用ux表示u对x的偏导数,uy、vx、vy类似, 学过柯西黎曼方程吧:ux=vy,uy=vx, 对所给条件分别对x,y求偏倒得: uxvx=3x^26xy3y^2,uyvy=3x^26xy3y^2



2
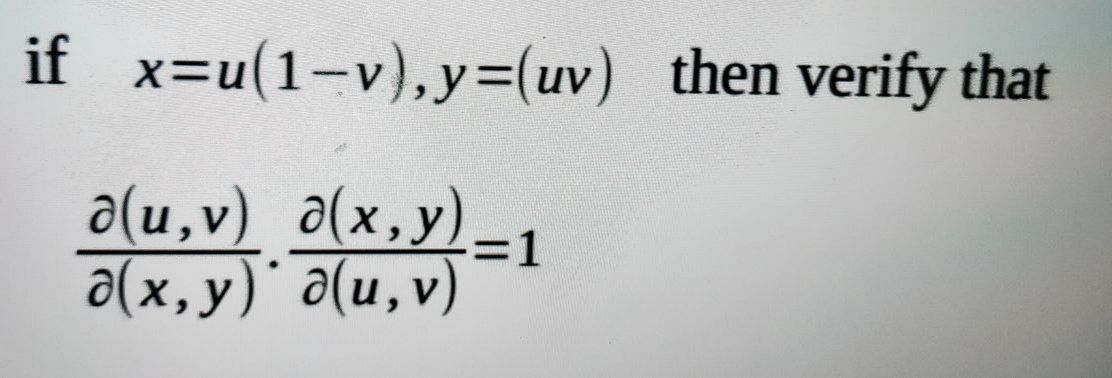



Answered If X U 1 V Y Uv Then Verify That Bartleby
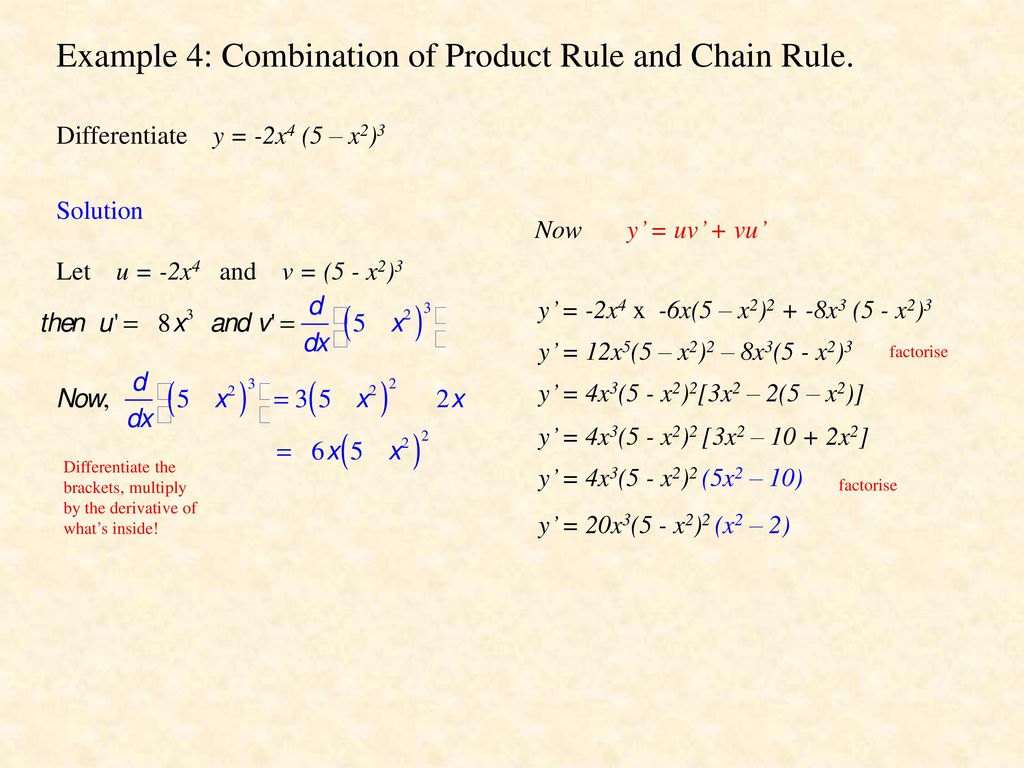



Differentiation Product Rule By Mr Porter Ppt Download
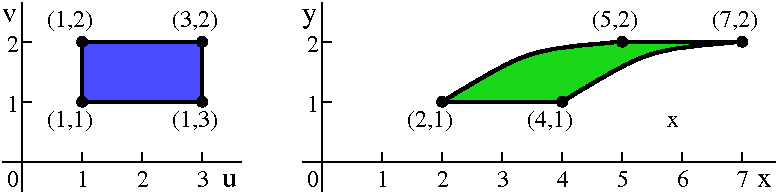



Math 251 Diary Fall 10



2
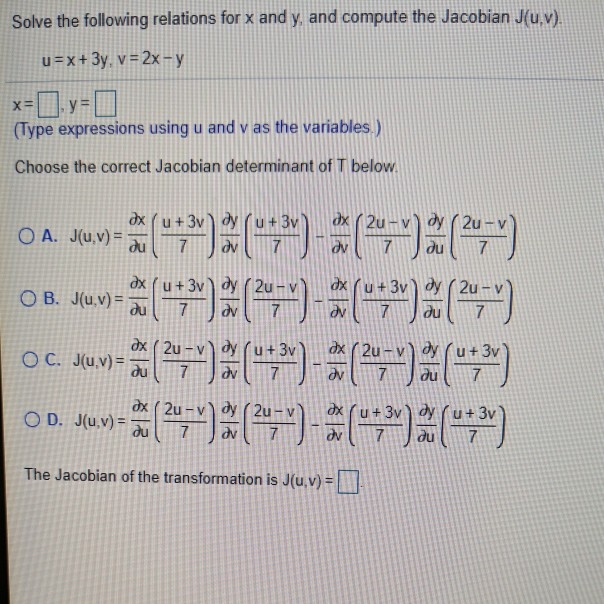



Solved Solve The Following Relations For X And Y And Chegg Com
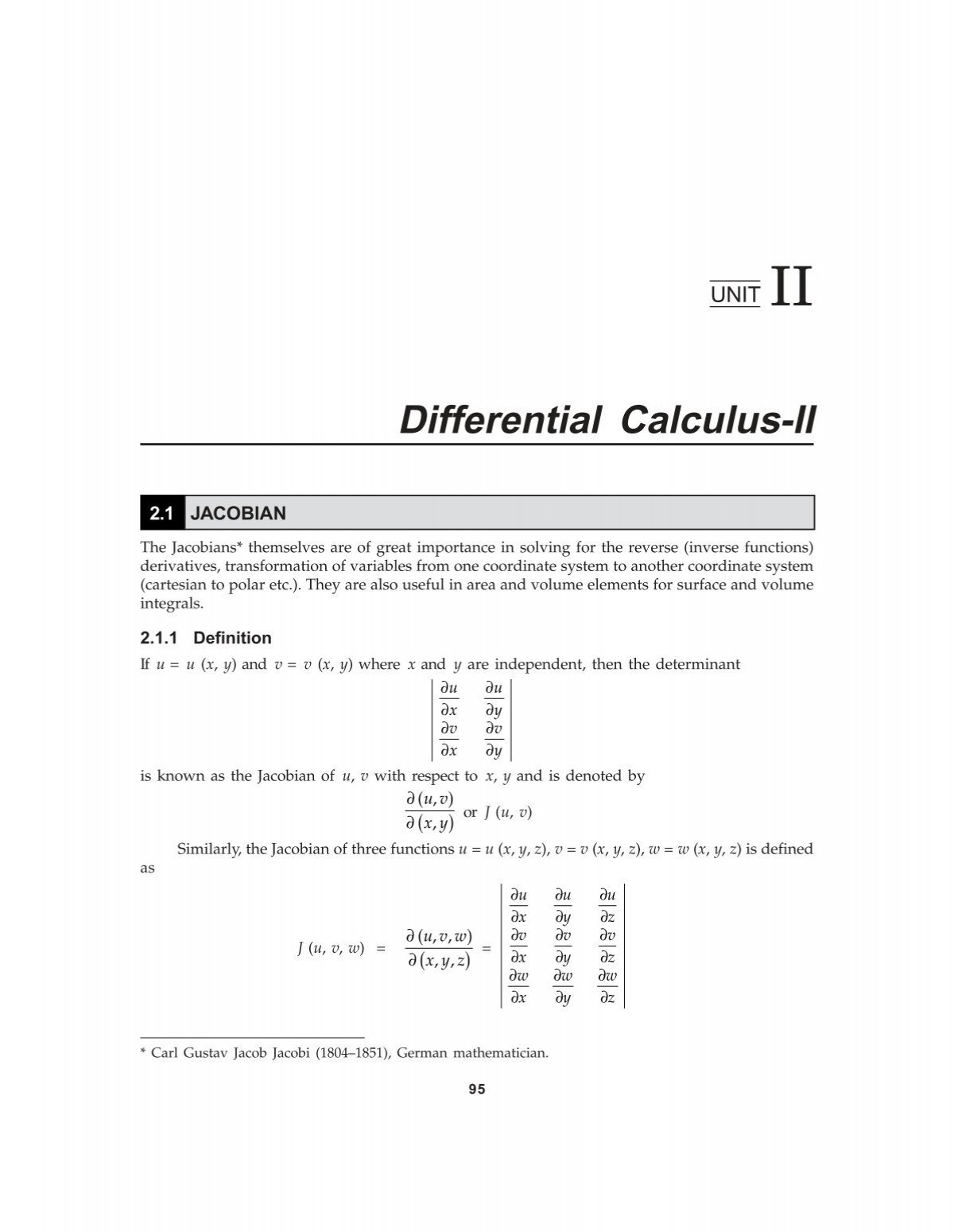



Differential Calculus Ii New Age International



Assignmentexpert Com



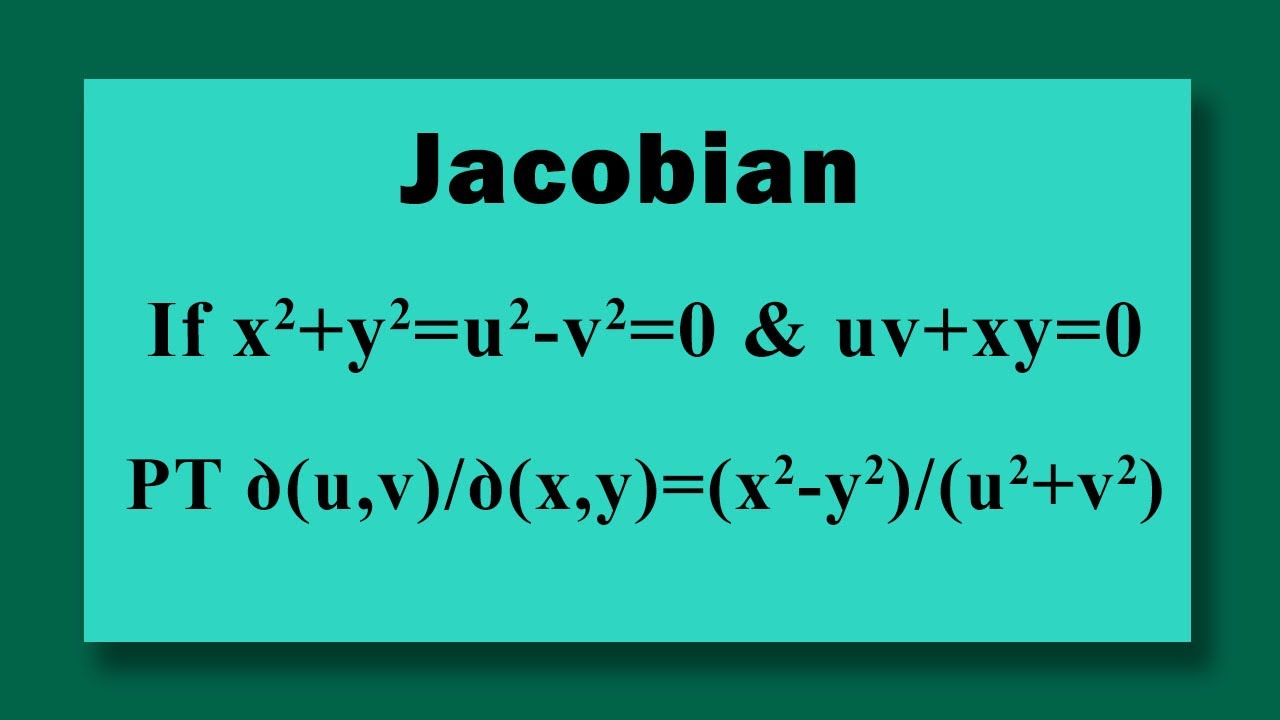
File



Jacobian If X 2 Y 2 U 2 V 2 0 Uv Xy 0 Prove That ꝺ U V ꝺ X Y X 2 Y 2 U 2 V 2 Youtube



2




Pdf Partial Derivatives 13 1 Functions Of Several Variables Joseph Feliz Academia Edu



If U V X Y X2 4xy Y2 And F Z U Iv Is An Analytic Function Of Z X Iy Find F Z Is Terms Of Z Brainly In
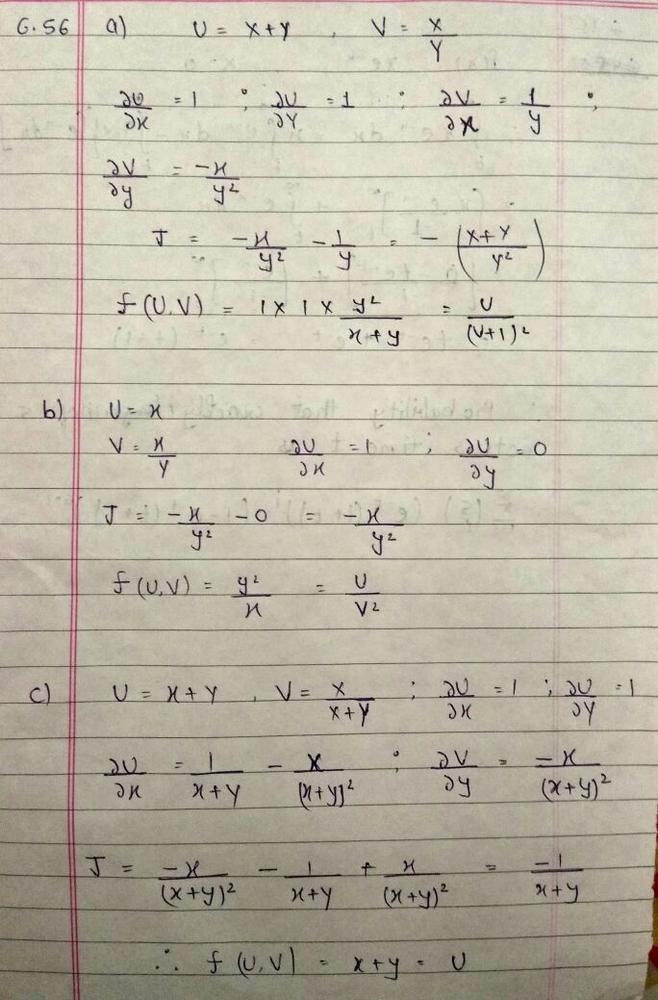



If X And Y Are Independent And Identically Distributed Uniform Random Variables On 0 1 Compute The Joint Density Of A U X Y V X Y B U X V X Y C U X Y V X X Y Homework Help



Mathscool Com
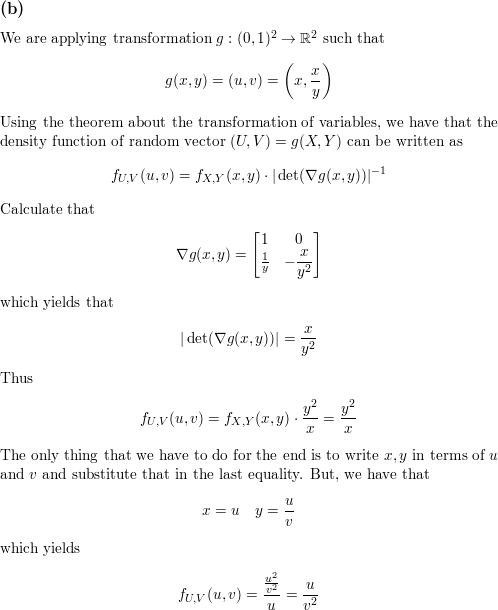



If X And Y Are Independent And Identically Distributed Uniform Random Variables On 0 1 Compute The Joint Density Of A U X Y V X Y B U X V X Y C U X Y V X X Y Homework Help
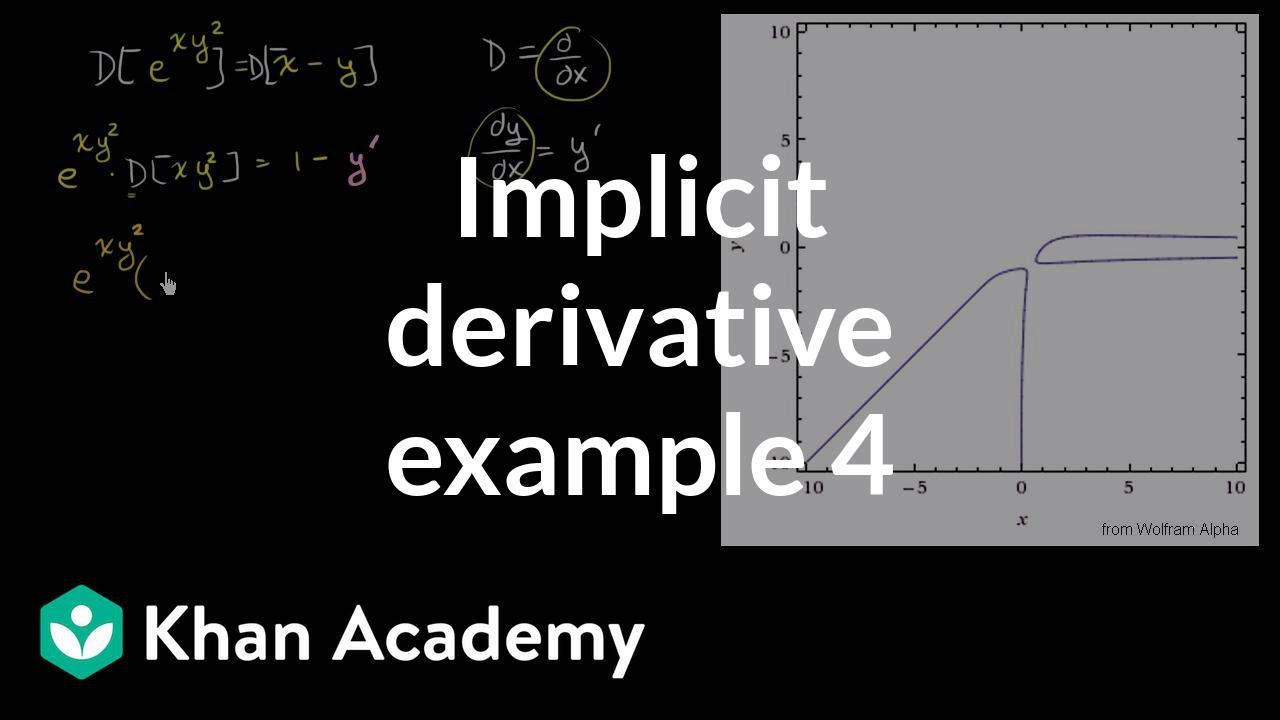



Implicit Differentiation Advanced Example Video Khan Academy



2
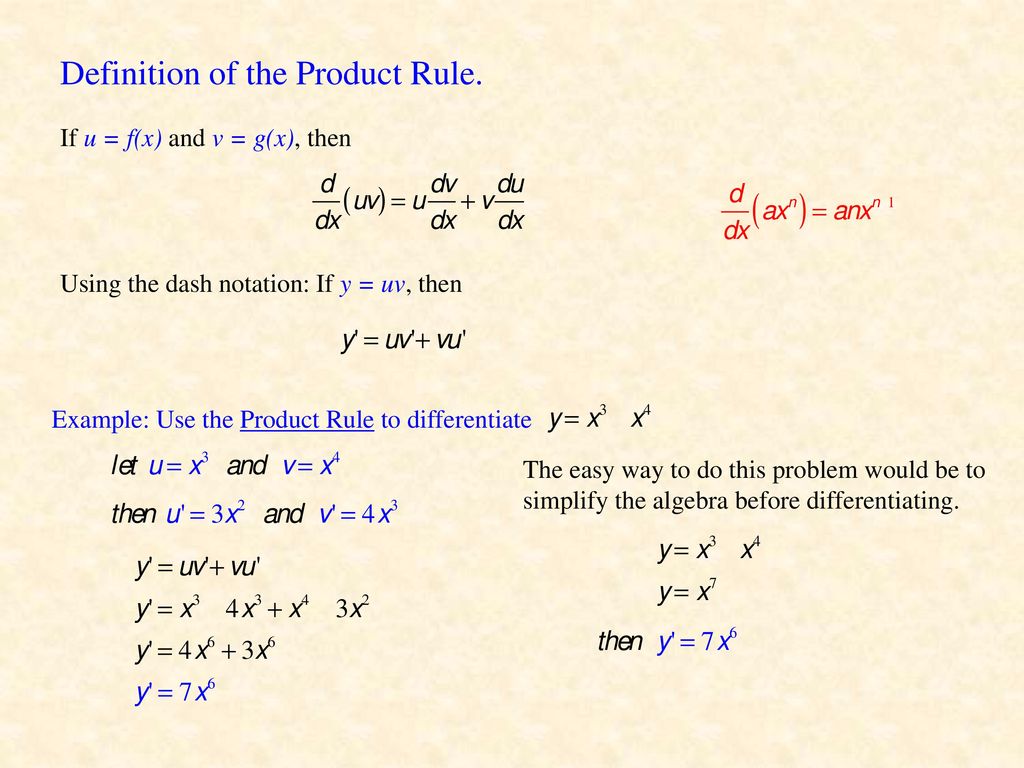



Differentiation Product Rule By Mr Porter Ppt Download




Divergence Theorem Of Gauss Example 1 Example 2
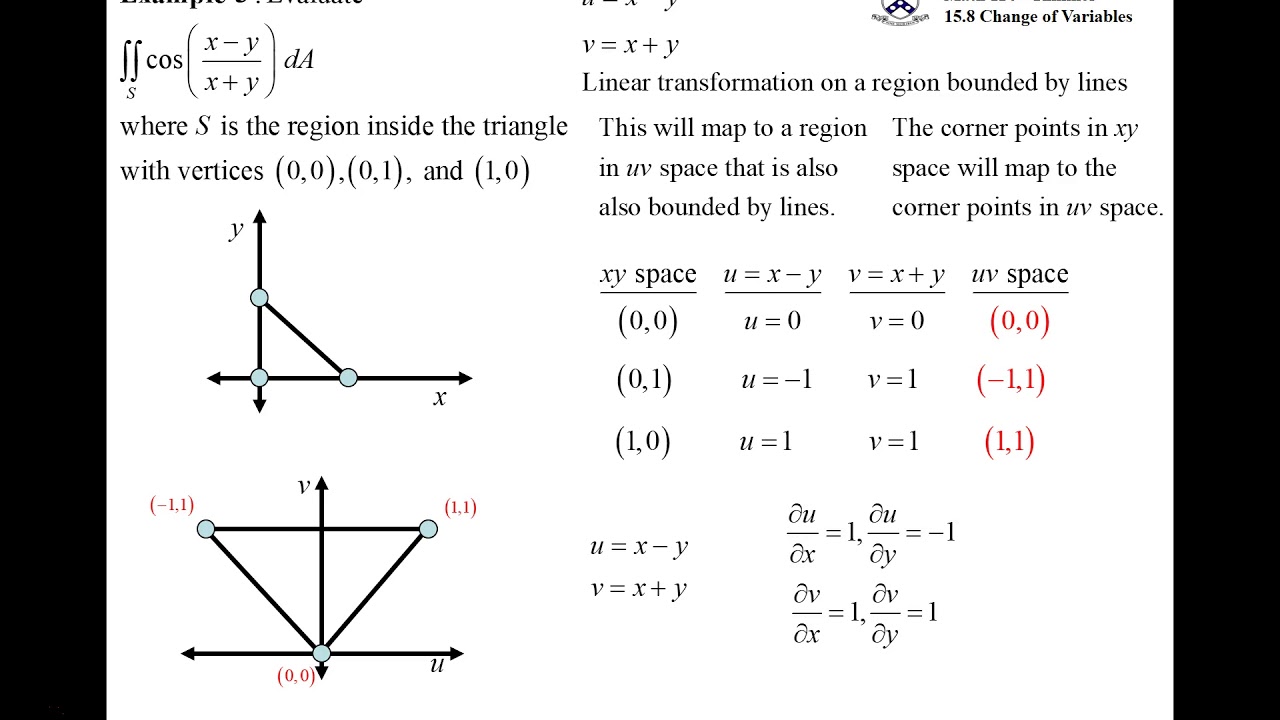



Double Integration Change Of Variable Example 3 Converting Region By Converting Corner Points Youtube




Answered 9 Let R Be The Region In The First Bartleby




15 Multiple Integrals Multiple Integrals 15 9 Change




Solved Let H Fixy 2 Where X Uv Cos 4 Y Uv Sin Andz Z V Calculate And At U V D 12 6 1 5x In Terms Of The Partial




Solved Example 4 A If Z F X Y X2 4xy Y Find The Chegg Com
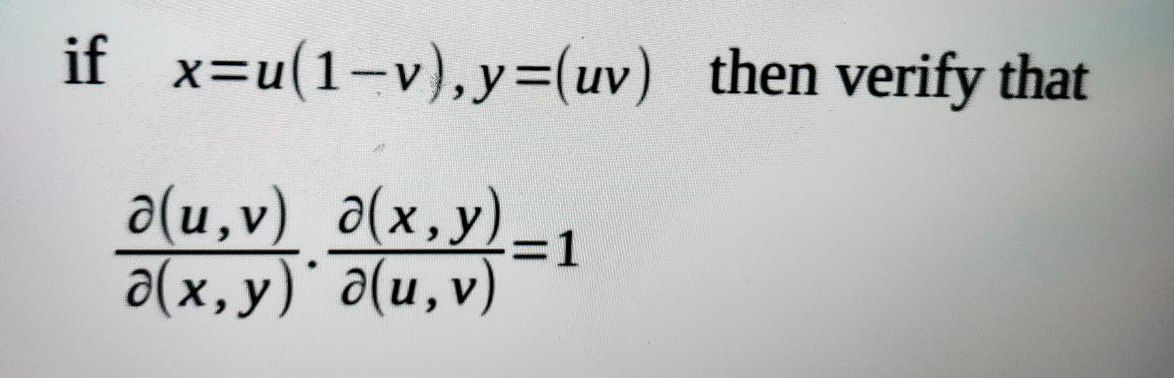



Answered If X U 1 V Y3 Uv Then Verify That Bartleby




15 Multiple Integrals Multiple Integrals 15 9 Change




Differentiation Product Rule By Mr Porter Ppt Download



2




Tinkutara Equation Editor Math Forum Question




Consider Evaluating The Integral I Integral 2 Y 0 Chegg Com



Mathematics Pitt Edu



2



2



2




A6jykahfrab0ym



Introduction To Coordinate Geometry




Jacobian Find ꝺ U V ꝺ R 8 If U 2xy V X 2 Y 2 Where X Rcos8 Y Rsin8 Youtube




J Osxal Osx Y 1 Q F X Y 24xy 1 Find Pc Y A Find Joint Density 111 Homeworklib
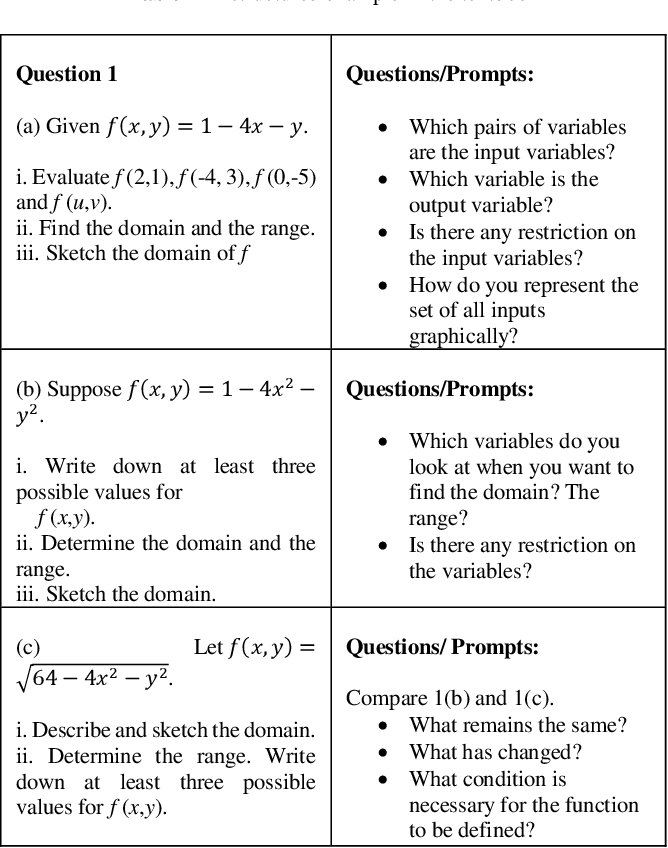



Learning Functions Of Two Variables Based On Mathematical Thinking Approach Semantic Scholar




Pure Mathematics 1 Advance Level Maths Pdf Txt




Find The Minimum Value Of X 2 4xy 4y 2 2z 2 Given That Xyz 32 Mathematics Stack Exchange




Calculate Iint D 2x Cos 2 X Y X 𝑑𝑥𝑑𝑦 Where D Is A Rectangle With Corners At P 6 2 P 6 P 6 4 P 6 P 4 4 P 4 And P 4 2 P 4 Mathematics Stack Exchange




Some Issues On The Automatic Computation Of Plane Envelopes In Interactive Environments Sciencedirect



Cauchy Riemann Show That U V X Y X2 4xy Y2 Find F Z Youtube



2



2




The Surface Z Xsqrt X Y Intersects The Plane Y 3 Along A Curve C How Do You Find The Parametric Equations For The Tangent Line To This Curve At The Point P 1 3 2 Socratic




Solutions Homework Sections Pdf Free Download




15 Multiple Integrals Multiple Integrals 15 9 Change




Chap 1



2



If U V X Y X2 4xy Y2 And F Z U Iv Is An Analytic Function Of Z X Iy Find F Z Is Terms Of Z Brainly In



2



2



2




14 7 Change Of Variables In Multiple Integrals Jacobians Mathematics Libretexts



2




Prove That The Conic X 2 4xy Y 2 2x y 11 0 Is A Hyperbola And Find The Centre H K Mathematics Stack Exchange




Exercise




1 Consider Two Random Variables X And Y With Joint Density Function F X Y 12xy 1 Y 0 X 1 0 P 1 Otherwise Homeworklib




Jpirasutog1blwh 最も好ましい X Y 2 X Y 2 Is Equal To X Y Z 0 Then X 2 Xy Y 2 Is Equal To




The Derivative Rules For Multivariable Functions Stated Theorem 10 On Page 151 Are Analogous To Derivative Rules From Single Variable Calculus Example Ppt Download



3 1 63 46 8080
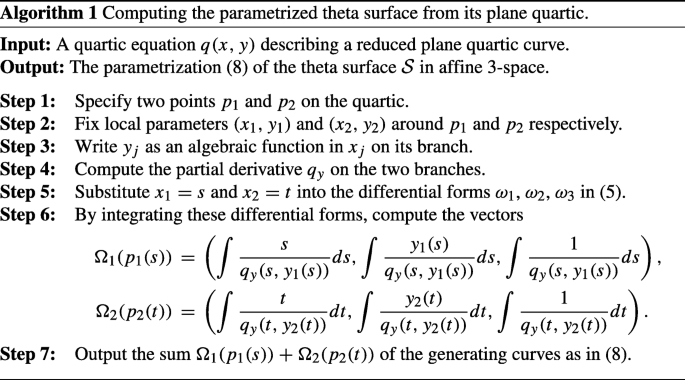



Theta Surfaces Springerlink



If Math 3x 4y Sqrt Xy Math How Can You Prove That Math X 2 Y 2 Xy Math Quora




Solved 11 A Find The Analytic Function F Z U Iv Chegg Com



2




Multiple Integrals H 2 Y Are Continuous Functions On C D And Let F X Y Be A Function Defined On R Then Pdf Free Download




Thomas Calculus 11e 8 1262 Pages 151 0 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5




Math Pdf Complex Analysis Holomorphic Function



2



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿